Crustacean Cardioactive Peptide CCAP
CAS No. 309247-84-5
Crustacean Cardioactive Peptide CCAP( —— )
Catalog No. M30112 CAS No. 309247-84-5
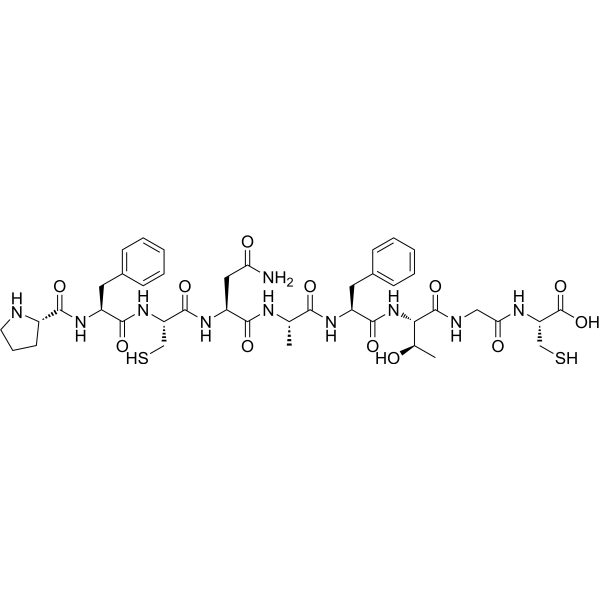
Crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) is a highly conserved, amidated cyclic nonapeptide with the primary structure PFCNAFTGC-NH2 (ProPheCysAsnAlaPheTyrGlyCys-NH2) and a disulfide bridge between Cys3 and Cys9. It is found in crustaceans and insects where it behaves as a cardioaccelerator, neuropeptide transmitter for other areas of the nervous system and a hormone.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 284 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 498 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCrustacean Cardioactive Peptide CCAP
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCrustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) is a highly conserved, amidated cyclic nonapeptide with the primary structure PFCNAFTGC-NH2 (ProPheCysAsnAlaPheTyrGlyCys-NH2) and a disulfide bridge between Cys3 and Cys9. It is found in crustaceans and insects where it behaves as a cardioaccelerator, neuropeptide transmitter for other areas of the nervous system and a hormone.
-
DescriptionCrustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) is a highly conserved, amidated cyclic nonapeptide with the primary structure PFCNAFTGC-NH2 (ProPheCysAsnAlaPheTyrGlyCys-NH2) and a disulfide bridge between Cys3 and Cys9. It is found in crustaceans and insects where it behaves as a cardioaccelerator, neuropeptide transmitter for other areas of the nervous system and a hormone.(In Vitro):Ultrabithorax and Abdominal-A are not necessary for specification of the CCAP-interneurons, but are absolutely required to prevent the death by apoptosis of the CCAP-efferent neurons.(In Vivo):CCAP, FMRFamide and SALDKNFMRFamide increase the mosquito antennal accessory pulsatile organ (APO) and heart contraction rates, increase hemolymph flow velocity in the antennal space.
-
In VitroUltrabithorax and Abdominal-A are not necessary for specification of the CCAP-interneurons, but are absolutely required to prevent the death by apoptosis of the CCAP-efferent neurons.
-
In VivoCCAP, FMRFamide and SALDKNFMRFamide increase the mosquito antennal accessory pulsatile organ (APO) and heart contraction rates, increase hemolymph flow velocity in the antennal space.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number309247-84-5
-
Formula Weight959.1
-
Molecular FormulaC42H58N10O12S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 50 mg/mL (52.13 mM; Need ultrasonic);H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical NameSequence:Pro-Phe-Cys-Asn-Ala-Phe-Thr-Gly-Cys
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
Suggs JM, et al. CCAP and FMRFamide-like peptides accelerate the contraction rate of the antennal accessory pulsatile organs (auxiliary hearts) of mosquitoes. J Exp Biol. 2016 Aug 1;219(Pt 15):2388-95.
molnova catalog



related products
-
27-O-acetyl-withafer...
27-O-acetyl-withaferin A is a natural product.
-
Ebopiprant
Ebopiprant (OBE022) is an orally available, selective and potent prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) receptor antagonist that interferes with the binding of PGF0126α to the FPR and can be used in the study of obesity.
-
D-Pyroglutamic acid
D-Pyroglutamic acid (PCA) is a cyclic derivative of glutamic acid physiologically present in mammalian tissues. It has been shown that PCA releases GABA from the cerebral cortex and displays anti-anxiety effects in a simple approach-avoidance conflict situation in the rat.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


